Create an External Schema
This topic describes how to create an external schema through a DW service unit console or by using a Terraform script.
Before you start
Ensure the following:
-
A DW service unit is available in your environment. For details about how to create a DW service unit, see Create a DW Service Unit.
-
A database exists in the target DW service unit. For details about how to create a database, see Create a Database.
-
You have the credentials of a DW user (or cloud account) with access to the target DW service unit.
Use the DW service unit console to create an external schema
Use a workbook
-
Sign in to the DW service unit console.
infoIf you have signed in to the Relyt global console, navigate to the DW Service Units page. Locate your target service unit and click Connect to access its console.
-
In the left sidebar, choose Workbooks. On the page that appears, click the + Workbook button at the upper-right corner.
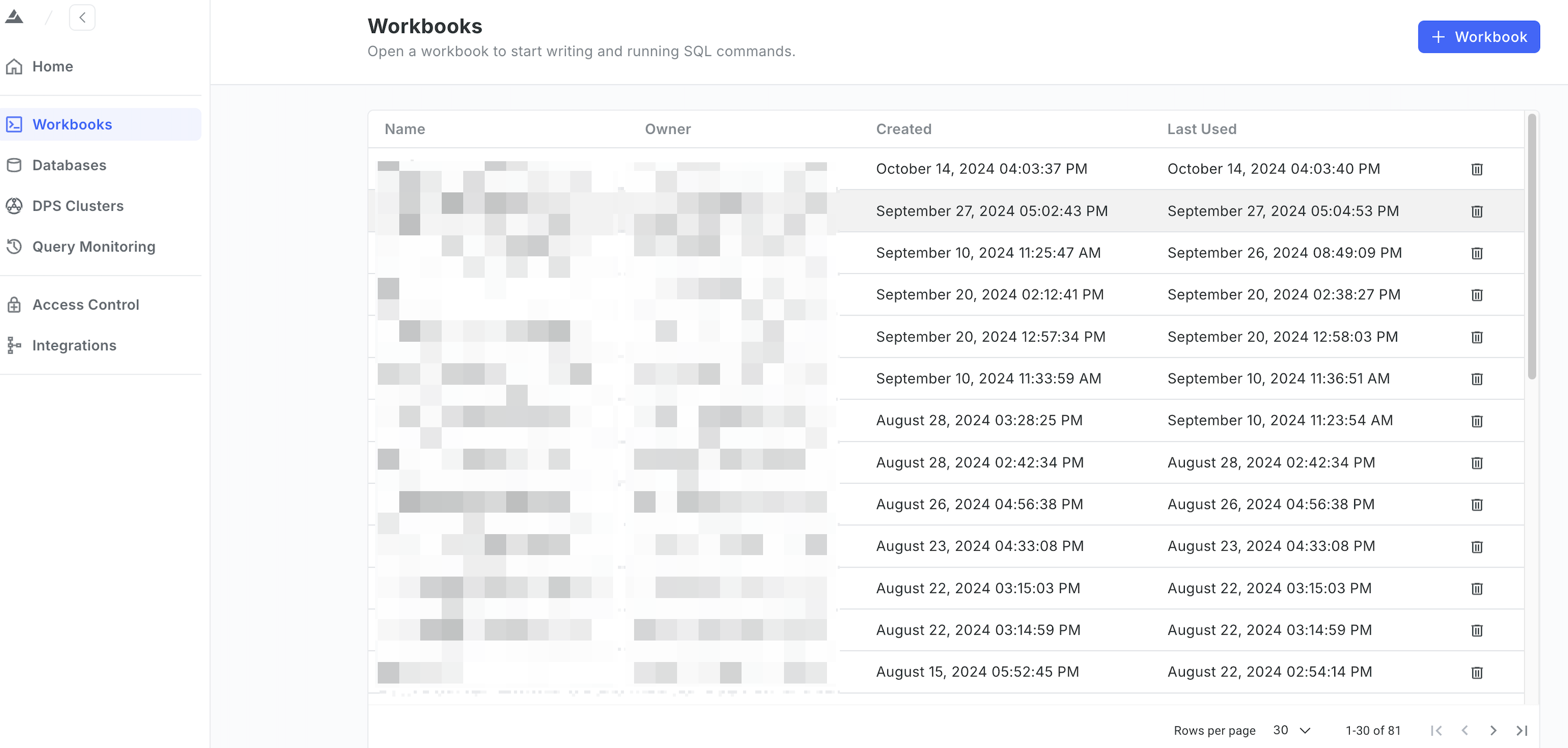
-
In the SQL editor, write the
CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMAcommand, select the database, set the DPS cluster to an Extreme DPS cluster, and click the Run button.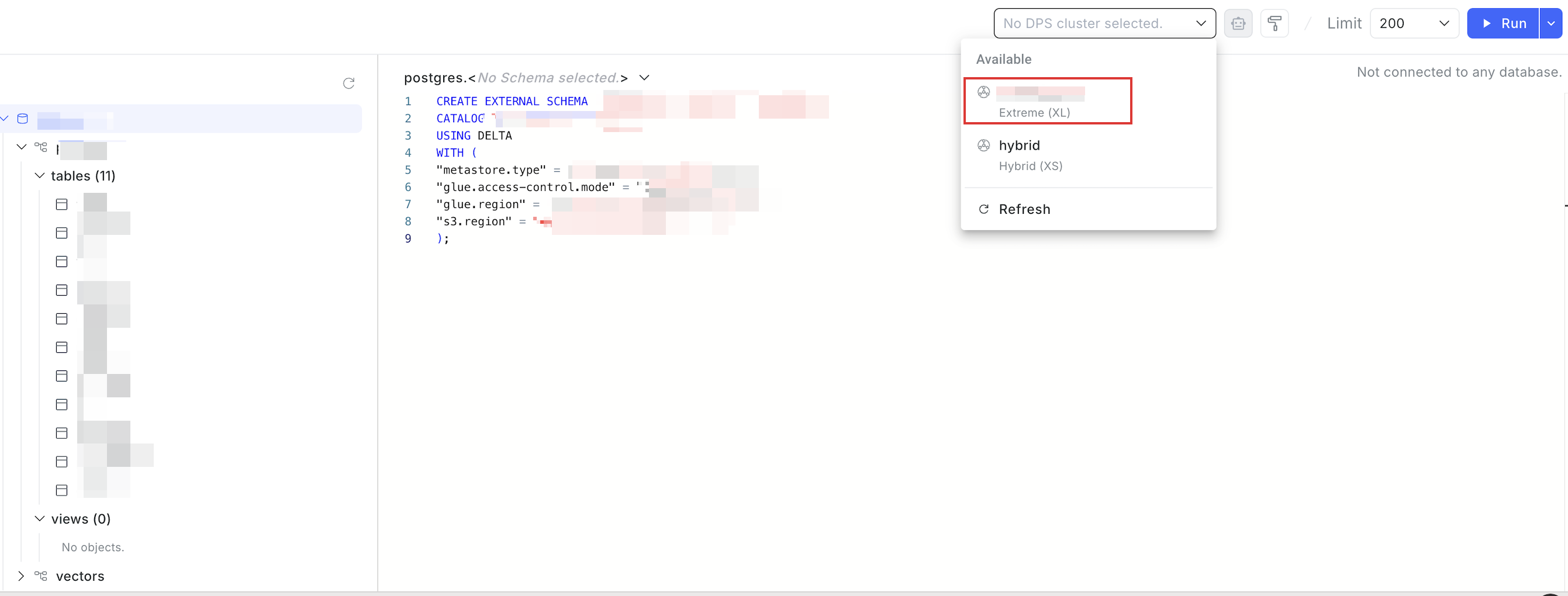
Following is an example SQL command:
CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMA '<external_existing_schema_name>'
CATALOG '<external_catalog_name>'
USING DELTA
WITH (
"metastore.type" = '<external_metastore_type>',
"glue.access-control.mode" = "lake-formation",
"glue.region" = '<external_glue_catalog_region>',
"s3.region" = '<storage_aws_region>'
);For information about the parameter description, see CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMA.
Note thatThe combined length of the catalog name and the schema name must not exceed 127 characters.
TroubleshootingIf you encounter an internal error or a schema name-related issue when running
CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMA, verify your parameter and name settings by following the guidance in Usage notes.
Follow the wizard
For details, see Step 6 in topic "Configure Access to S3 Data Sources Through Integration with AWS Lake Formation".
Use a Terraform script to create an external schema
This section describes how to run a Terraform script to create an external schema.
Before you start
To use the script, ensure you have obtained the following information:
-
An API key:
How to obtain: Sign in to your Relyt console, choose API Keys from the top navigation bar, and click + API Key to create one.
-
An pair of access key and secret key:
How to obtain:
-
Sign in to your DW service unit console and choose Access Control > Open API.
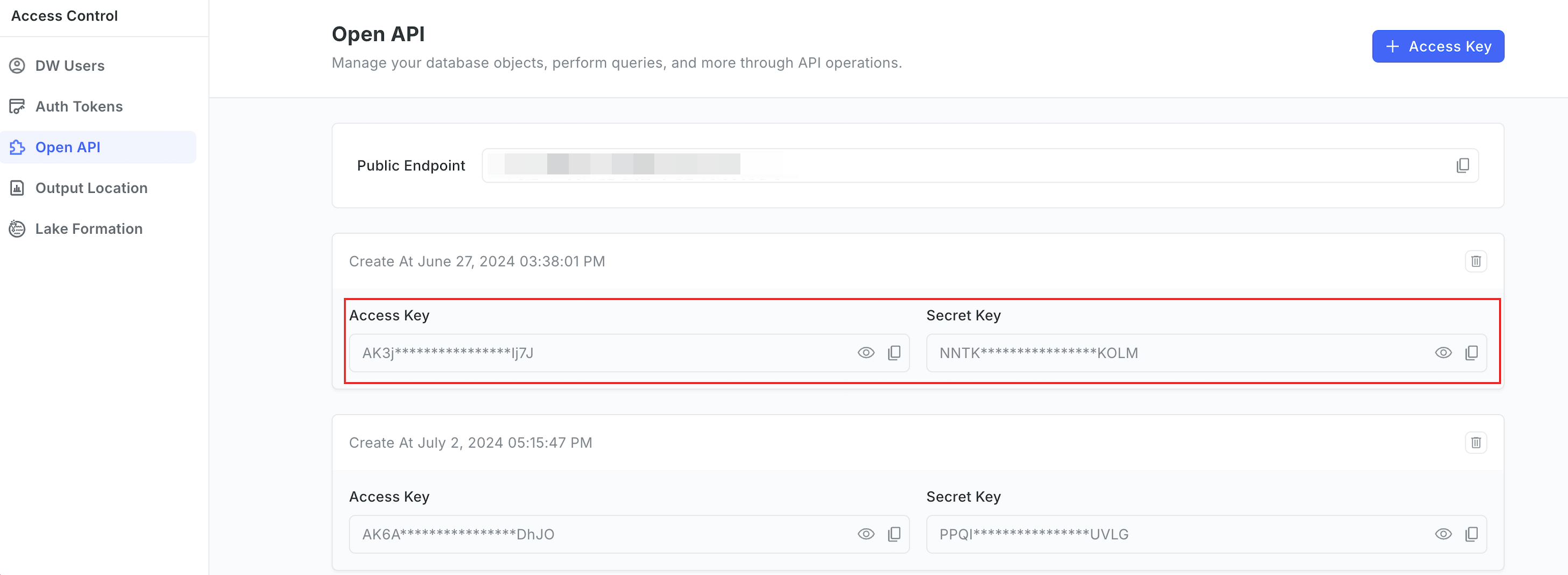
-
Copy the access key and secret key.
If no access key/secret key pair is available, click + Access Key to generate one.
-
-
The endpoint for accessing the DW service unit
For details about how to check the endpoints, see Query Endpoints.
Procedure
-
Download the latest Terraform script.
Following is a code snippet example from the module for creating an external schema. Configure the parameters according to your needs.
terraform {
required_providers {
relyt = {
source = "relytcloud/relyt"
}
}
}
provider "relyt" {
role = "SYSTEMADMIN"
data_access_config = {
access_key = "<access_key>"
secret_key = "<secret_key>"
endpoint = "<endpoint>"
}
}
resource relyt_dwsu_external_schema ex_schema {
name = "<external_schema_name>"
database = "<database_name>"
catalog = "<catalog_name>"
table_format = "DELTA"
properties = {
"metastore.type" = "<external_metastore_type>"
"glue.region" = "<external_glue_catalog_region>"
"s3.region" = "<storage_aws_region>"
"glue.access-control.mode" = "<access_control_mode>"
}
}Field description:
Field Description sourceThe name of the Relyt plugin. It is fixed to relytcloud/relyt.roleThe system role of your Relyt cloud account. It is fixed to SYSTEMADMIN.access_keyThe access key for Open API operations. secret_keyThe secret key for Open API operations. endpointThe endpoint for accessing the DW service unit. nameThe name of the external schema. The schema name must be consistent with the name of the target schema that exists in the external catalog.
Note that the combined length of thecatalogandschemavalues must not exceed 127 characters.databaseThe name of the database to create. catalogThe name of the catalog.
Note that the combined length of thecatalogandschemavalues must not exceed 127 characters.table_formatThe data format, fixed to DELTA.metastore.typeThe type of the metastore, fixed to glue.glue.regionThe region where the metastore resides. s3.regionThe region where the S3 bucket that stores the source data resides. glue.access-control.modeThe access control mode, fixed to lake-formation.
For details about how to obtain the
access_key,secret_key, andendpoint, see the instructions provided in Before you start.TroubleshootingIf you encounter an internal error or a schema name-related issue when running
CREATE EXTERNAL SCHEMA, verify your parameter and name settings by following the guidance in Usage notes. -
Run the following command to export the auth key.
export RELYT_AUTH_KEY="<api_key>"Replace
<api_key>with the API key you have obtained. For details about how to obtain the API key, see the instructions provided in Before you start. -
Run the following command to initialize the Terraform working directory.
terraform init -
Run the following command to apply the module.
terraform apply --target=module.schema -
When prompted, enter
yesto confirm the operation.When information similar to the following is displayed, the external schema is created.
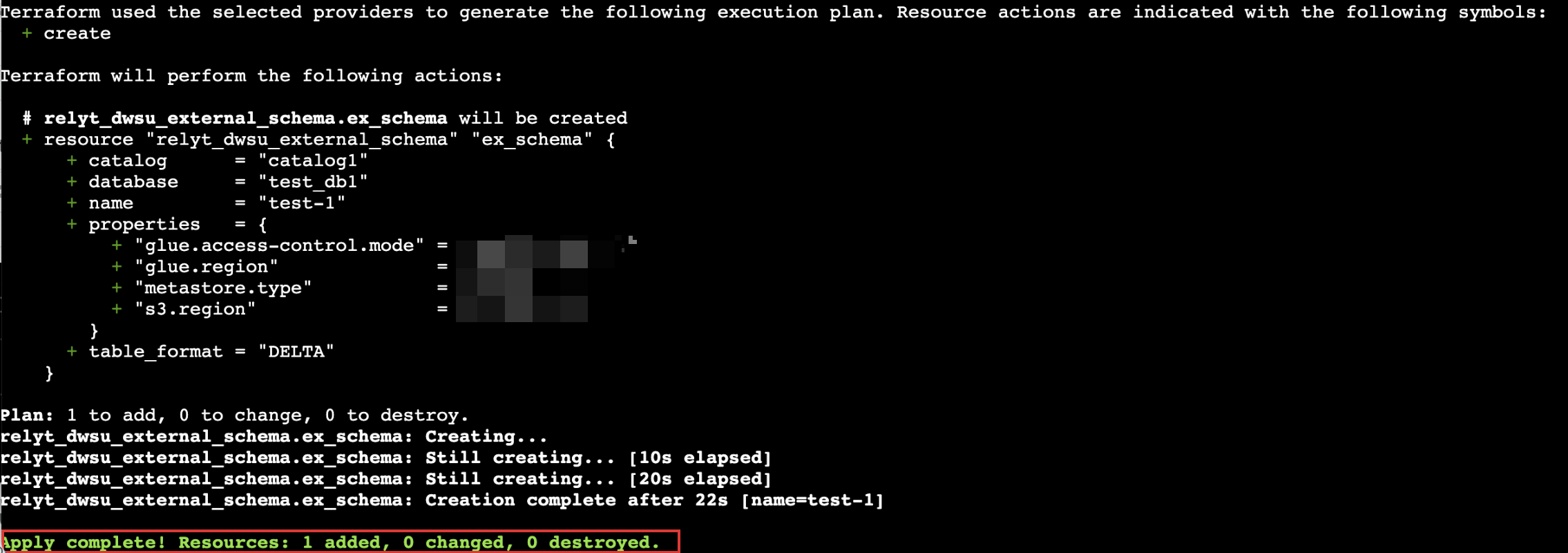
Usage notes
When running a Terraform script to create an external schema, errors may occur due to the following reasons:
-
Possible cause 1: Incorrect parameter settings
Solution:
-
Verify the settings for
metastore.typeandglue.access-control.mode. Currently,metastore.typemust be set toglue, andglue.access-control.modemust be set tolake-formation. -
Ensure that the
glue.regionands3.regionparameters are set to valid, non-null regions supported by the cloud provider.
-
-
Possible cause 1: Naming convention variations
Solution:
-
Ensure the combined length of the catalog name and external schema name does not exceed 127 characters.
-
Verify that the external catalog name only includes supported special characters:
~!@#$%^&*()-_=+[{]}\\|;:',<.>/?. Unsupported characters like double quotation marks (") are not allowed.
-